The Components Engineering Library
Site Navigation
| Vender Catalogs | ||
| Resistors | Capacitors | Inductors |
Inductors, Coils, Fixed
Inductors or Coils are passive devices used in electronics. Finding crosses or equivalent parts can be done. Just match the parameters.
Inductor (Fixed) (Radial) (AirCoil)
Making crosses for Inductor can be done by matching parameters. Our venders (left column) can help in making matches and purchases. The sales reps on the right column can find sources. Once Selected it is highly recommended that you acquire a sample from the manufacturer to try in your circuit.
Inductor (Henrys) Electrical Schematic Symbols
Click on Parameter or Units
| Parameter | Units |
|---|---|
| Inductance Value | Henry |
| Current Rating | Amperes (A) (mA) |
| Current Saturation | Amperes (A) (mA) |
| Series / Material (Core) |
The Unit of Inductance is Henry. This unit Varies.
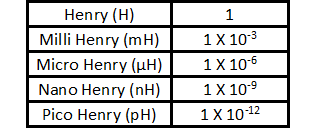
The value of Henry needs to match closely (see tolerance).
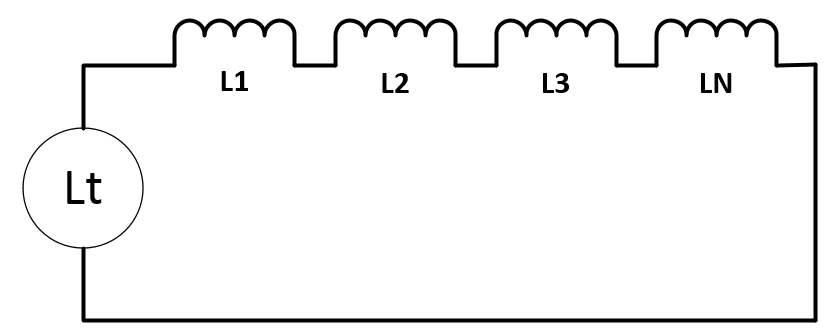
The value of henry must match the value of henry needed to achieve a matching device. If values cannot be matched. Connecting Inductors in parallel or series can achieve a matching value. Inductance in series is additive.
L total = L1 + L2 + L3 + Lm
Where Lm is mutual Inductance. Always test before buying large quantities.
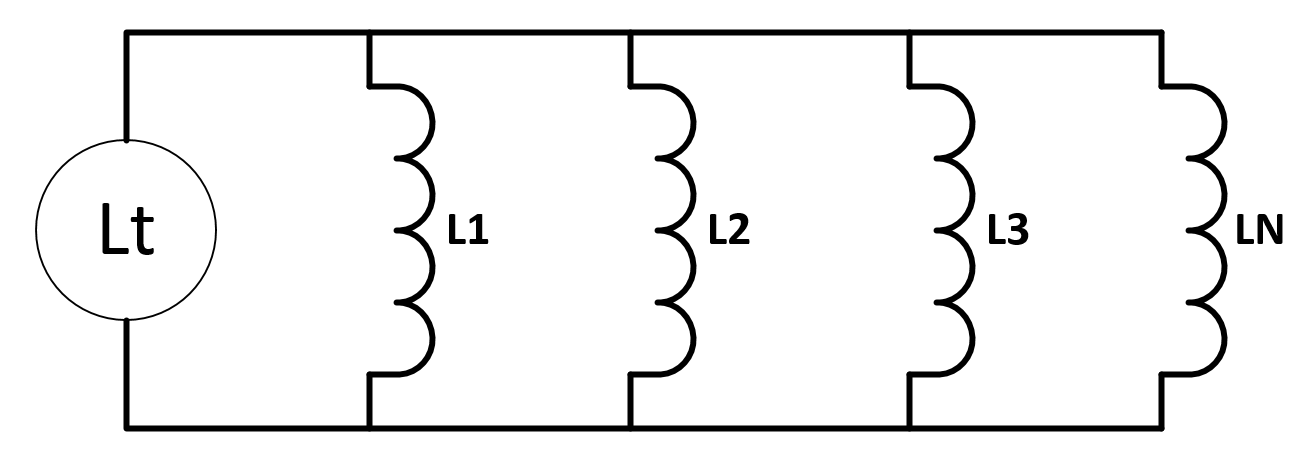
Inductance in Parallel can be calculated with this formula.
L total = 1/L1 + 1/L2 + 1/L3 + 1/Lm
Where Lm is mutual Inductance. Always test before buying large quantities.
Current Rating
Is the amount of current flow in an inductor must not be exceeded.
Rated in Amperes this parameter must be the same as previously used or more.
Current Saturation
Current Saturation of an Inductor is the state where increasing the current will not cause a change in magnetization (Inductance) . This parameter is important in component matching
DC Resistance
A perfect inductor has 0 ohm resistance. All inductor in the real world has some resistance that must be accounted for in circuit design and component matching.
Q @ Frequency
The Q Factor or quality factor is a dimensionless value which used to determine the amount of selectivity in radio circuits. It is important in other applications as well and an important parameter to match.
Self-Resonance
Another important parameter to consider when selecting a replacement inductor is Self-Resonance. Measured in Frequency (Hz).
Tolerance
It is important to match the “Tolerance” of the inductor. The Tolerance is the accuracy of the inductance value (Henry). The degree of Tolerance is measured in percent. Some timing circuits like oscillators may require a high tolerance for better precision.
Shielding
Depending on where the inductor is used Shielding may or may not be needed. If the circuit is already shielded the individual inductor may not need shielding.
Series / Material (Core) / Type
There are many types of inductors depending on the configuration of the outer layer windings or coil, and the inner portion material “Core”. I will show in pictures these different types.


